Introduction And Definition
* An array in C/C++ is a "collection of related data elements of the same type that are referenced by a common name or is a variable which can store multiple value at a same time of same data types.". Generally, it is just another data type, aggregate data type or derived data type.
* All the elements of an array occupy a set of contiguous memory locations and by using an index or subscript we can identify each element.
* For example, instead of declaring mark1, mark2, ..., markN to store and manipulate a set of marks obtained by the students in certain courses, we could declare a single array variable named mark and use an index, such as j, to refer to each element in mark. This absolutely has simplified our declaration of the variables.
* Hence, would refer to the element in the array mark. Thus by changing the value of j, we could refer to any element in the array, so it simplifies our declaration.
* For example, if we have 100 list of marks of integer type, we will declare it as follows:
If we have 100 marks to be stored, you can imagine how long we have to write the declaration part by using normal variable declaration?
* By using an array, we just declare like this:
This will reserve 100 contiguous/sequential memory locations for storing the integer data type.
Graphically can be depicted as follows:

Array can divided on the following categories :

Declaration:
Dimension refers to the array size that is how big the array is. A single dimensional array declaration has the following form:
Here, array_element_data_type declares the base type of the array, which is the type of each element in the array. array_size defines how many elements the array will hold. array_name is any valid C/C++ identifier name that obeys the same rule for the identifier naming.
For example, to declare an array of 20 characters, named character, we could use:

In this statement, the array character can store up to 20 characters with the first character occupying location character[0] and the last character occupying character[19].
Note:- The index runs from 0 to 19. In C/C++, an index always starts from 0 and ends with (array size-1). So,notice the difference between the arraysize and subscript terms.
Examples of the one-dimensional array declarations:
float price[10], yield;
char letter[70];
* The first example declares two arrays named x and y of type int. Array x can store up to 20 integer numbers while y can store up to 50 numbers.
* The second line declares the array price of type float. It can store up to 10 floating-point values.
* The third one declares the array letter of type char. It can store a string up to 69 characters. (Why 69? Remember, a string has a null character (\0) at the end, so we must reserve for it.)
Just like ordinary variables, arrays of the same data type can be declared on the same line. They can also be mixed with ordinary variables of the same data type like in the second line together with yield.
Initialization:
An array may be initialized at the time of its declaration, which means to give initial values to an array.
Initialization of an array may takes the following form:
For examples:
float x[5] = {5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 5.9, 6.1};
* The first line declares an integer array id and it immediately assigns the values 1, 2, 3, ..., 7 to id[0], id[1], id[2],..., id[6].
* In the second line assigns the values 5.6 to x[0], 5.7 to x[1], and so on.
* Similarly the third line assigns the characters ‘a’ to vowel[0], ‘e’ to vowel[1], and so on.
Note :- For characters we must use the single apostrophe (’) to enclose them. Also, the last character in the array vowel is the NULL character (‘\0’).
Initialization of an array of type char for holding strings may takes the following form:
For example, the array vowel in the above example could have been written more compactly as follows:
When the value assigned to a character array is a string (which must be enclosed in double quotes), the compiler automatically supplies the NULL character but we still have to reserve one extra place for the NULL.
int array[7]={1,2,3};
then
array[0]=1
array[1]=2
array[2]=3
& rest element assigned zero automatically i.e. array[5]=0 .
Case 2 :
int array[ ]={1,2,3};
then
array[0]=1
array[1]=2
array[2]=3
& rest element assigned any garbage value like array[5]=78346 .
Case 3 : Address of this array is differ by 4 in 32 bit compiler
i.e.
Address of array[0] is 0x8641 then address of array[1] is 0x8645.
(1) A pointer.
(2) A sized array (dimension is explicitly stated), e.g. s[20] or
(3) An unsized array (dimension is not stated), e.g. p[ ].
For example, to receive an array named x of type float in functions, we may declare any one of the following:
// Pointers, will be explained in another Module
// Sized array
// Unsized array
The following program segment illustrates the passing of an array address to a function using a pointer.
Here, the memory address of x is passed to the parameter pter, a pointer. Remember this; an array name (without the size) is the pointer to the first array’s element. We will discuss this in more detail later.
// function prototype
void func(float *);
int main()
{
float x[5];
// an array name (without the bracket) is
// the pointer to the first array element
func(x);
return 0;
}
// function definition
void func(float *pter)
{
return;
}
not 1 to 7.
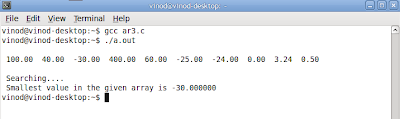
Output :
Output :
Exchanging Values of Variables :
You must use a third variable as in the following example:
third_var = num1;
//then assigns num2 to num1
num1 = num2;
//finally assigns third_var to num2
num2 = third_var;
Many algorithms (techniques) are available to perform sorting.We will discuss the sorting in details later.
Declaration:
* A set of string s can be stored in a two-dimensional character array with the left index specifying the number of strings and the right index specifying the maximum length of each string.
x[0][0]=1 x[0][1]=2 x[0][2]=3 x[0][3]=4
x[1][0]=5 x[1][1]=6 x[1][2]=7 x[1][3]=8
x[2][0]=9 x[2][1]=10 x[2][2]=11 x[2][3]=12
int x[3][4] = {{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8},{9,10,11,12}};
- If the number of values given is insufficient to fill in the whole array, an initial value of zero will be assigned to all those locations, which are not given initial values explicitly.
- For example:
int x[3][4]={0}; //all array elements will be 0
An array of string can also be initialized. For example, in the following declaration:
char name[4][10] = {"Sally","Joyce", "Lisa", "Alice"};
- The values assigned are as follows:
name[0] = "Sally" name[1] = "Joyce"
name[2] = "Lisa" name[3] = "Alice"
Data_type name[size1][size2]...[sizeN];
- For example:


















0 comments:
Post a Comment